|
|
8 months ago | |
|---|---|---|
| .github/workflows | 2 years ago | |
| .vscode | 10 months ago | |
| __pycache__ | 2 years ago | |
| controlplane | 8 months ago | |
| function_modules | 8 months ago | |
| .dockerignore | 10 months ago | |
| .gitignore | 2 years ago | |
| DAGit-HiPC-2023.pdf | 2 years ago | |
| Dockerfile | 10 months ago | |
| build-mongod.sh | 8 months ago | |
| dagit.log | 10 months ago | |
| docker-compose.debug.yml | 10 months ago | |
| docker-compose.yml | 10 months ago | |
| get-pip.py | 10 months ago | |
| load_test.py | 10 months ago | |
| readme.md | 10 months ago | |
| requirements.txt | 10 months ago | |
readme.md
DAGit
Currently being developed by Anubhav Jana along with Prof Puru IITB
This serverless FaaS platform supports individual function registrations, DAG registrations, Trigger registrations associated with DAGs/functons. This platform also supports various DAG primitives which is provided in this document for reference.
Guide: Register a Function
This section will guide you how to register a function. The following pre-requites are to be fulfilled before you register a function
-
DockerFile - based on which the image will be build to run your function
-
Python file - application logic to run the action/function (Here, in this example this is "test.py")
-
requirements.txt - add all dependant pip packages in this file. In case you dont have any library dependancies,submit a blank requirements.txt
You must have the above 3 files before you register the function
Following is the sample code register_function.py to register a function. This will create a new function named "testaction" and register it onto our function store handled by us. The url endpoint is: /regster/function/function_name
register_function.py
import requests
import sys
import json
def server():
url = "http://127.0.0.1:5001/register/function/testaction"
files = [
('pythonfile', open(sys.argv[1],'rb')),
('dockerfile', open(sys.argv[2],'rb')),
('requirements.txt', open(sys.argv[3],'rb'))
]
reply = requests.post(url = url,files = files,verify=False)
print(reply.json())
def main():
server()
if __name__=="__main__":
main()
- Usage: python3 register_function.py test.py Dockerfile requirements.txt
Guide: Register a DAG
This section will guide you how to register a DAG. The following pre-requites are to be fulfilled before you register a DAG
- dag.json - a JSON specification file to define the DAG. Accepted DAG Format and a sample example is provided in this readme file itself.
Following is the sample code dag_register.py to register a DAG. This will register a new DAG onto our DAG store handled by us. The url endpoint is: /regster/dag
dag_register.py
import requests
import sys
import json
def server():
url = "http://127.0.0.1:5001/register/dag"
input_json_file = open(sys.argv[1])
params = json.load(input_json_file)
reply = requests.post(url = url,json = params,verify=False)
print(reply.json())
def main():
server()
if __name__=="__main__":
main()
- Usage: python3 dag_register.py dag.json
Guide: Register a Trigger
This section will guide you how to register a trigger. The following pre-requites are to be fulfilled before you register a trigger
- trigger.json - a JSON specification file to define the trigger. Accepted DAG Format and a sample example is provided in this readme file itself.
Accepted Trigger Format
DAG specification includes both control dependancy as well as the control dependancy
Trigger Fields
-
"trigger_name" : Name of the trigger. Type accepted is string
-
"type": Type specifies whether the trigger is for function or dag. Accepted values are "dag" and "function"
-
"trigger": Specifies the endpoint route
-
"dags": If "type" field is specified as "dag","dags" will accept a list of dags to trigger (type = list). Else keep it as ""
-
"functions": If "type" field is specified as "function","functions" will accept a list of functions to trigger (type = list). Else keep it as ""
Example format of trigger.json
{
"trigger_name": "mydagtrigger",
"type":"dag",
"dags": ["odd-even-test","dummy-dag"],
"functions":""
}
{
"trigger_name": "myfunctiontrigger",
"type":"function",
"dags":"",
"functions": ["odd-even-action"]
}
Following is the sample code trigger_register.py to register a trigger. This will register a new trigger onto our Trigger store handled by us. The url endpoint is: /regster/trigger
trigger_register.py
import requests
import sys
import json
def server():
url = "http://127.0.0.1:5001/register/trigger/"
input_json_file = open(sys.argv[1])
params = json.load(input_json_file)
reply = requests.post(url = url,json = params,verify=False)
print(reply.json())
def main():
server()
if __name__=="__main__":
main()
- Usage: python3 trigger_register.py trigger.json
List of triggers
-
http://127.0.0.1:5001/register/function/<function_name>
-
http://127.0.0.1:5001/run/<trigger_name>
-
http://127.0.0.1:5001/view/<dag_id>
-
http://127.0.0.1:5001/view/activation/<function_activation_id>
-
http://127.0.0.1:5001/view/dag/<dag_name>
Supported DAG Primitive
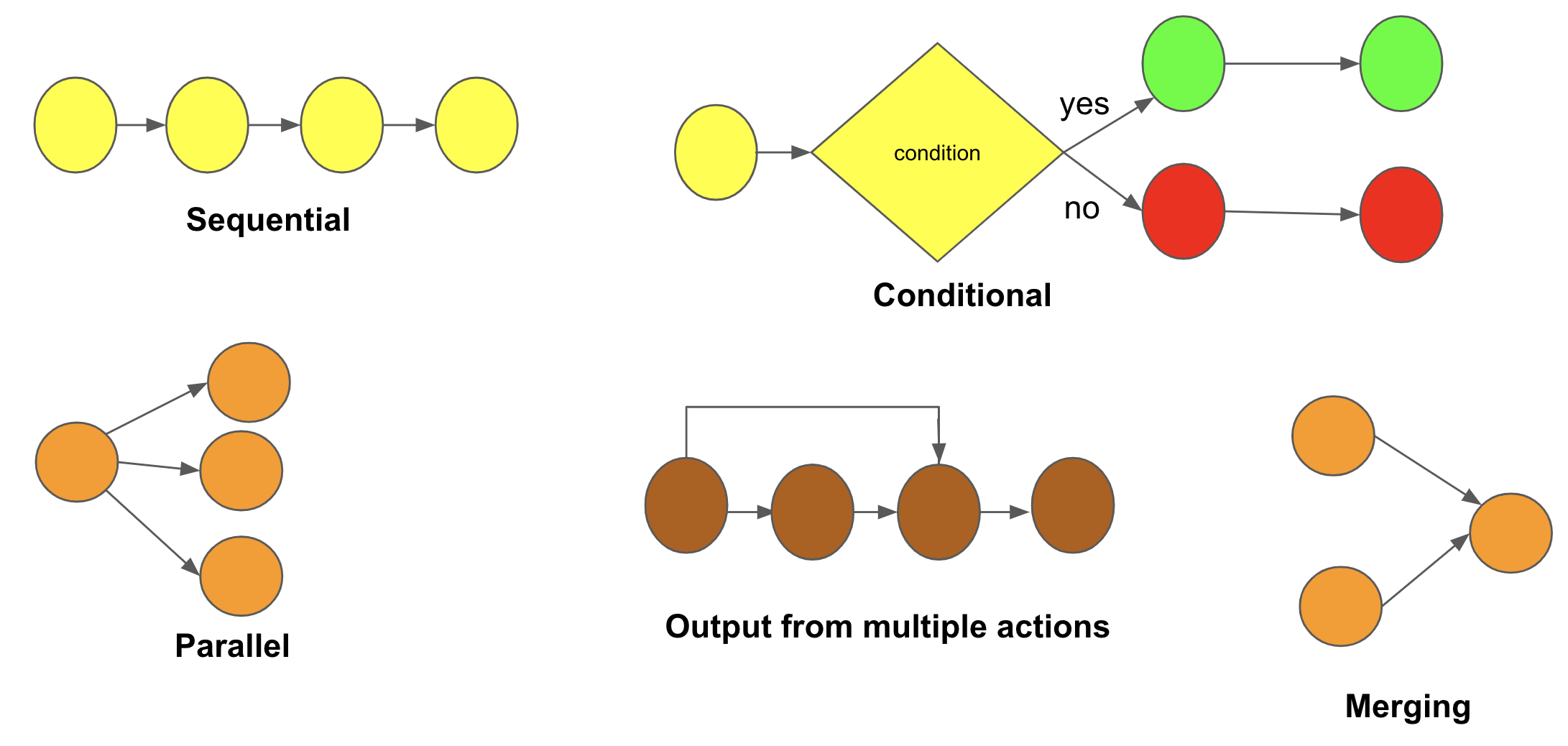
Accepted DAG Format
DAG specification includes both control dependancy as well as the control dependancy
DAG Fields
-
"name" : Name of the DAG
-
"node_id": Name of the function/action
-
"node_id_label": Name you want to give to the node
-
"primitive": Type of primitive the action supports - condition,parallel,serial(sequential)
-
"condition": If primitive type is "condition", then you should provide the following fields "source", "operator" and "target", else you should leave it as ""
-
"source": Specify any one of the response keys of the current node_id. For e.g. if one of the keys in response json is "result", and you want to provide a condition that if result=="even", then specify "source" as "result" and "target" as "even"
-
"operator": Mathematical operations like "equals", "greater_than" , "less_than", "greater_than_equals", "less_than_equals" are accepted.
-
"target": Specify the target value. It can accept both integer and string.
-
"next": Specify the name of next node_id to be executed. If primitive = "parallel", "next" will take list of node_ids, else it will accept a single node_id in "" format. If this is the last node_id(ending node of the workflow), keep it as "".
-
"branch_1": Specify node_id if primitive == condition else keep "". This is the target branch which will execute if condition is true
-
"branch_2": Specify node_id if primitive == condition else keep "". This is the alternate branch which will execute if condition is false
-
"arguments": Keep it blank for each node_id. It will get populated with json when the DAG is instantiated with the trigger
-
"outputs_from": Specify the list of node_id/node_ids whose output current node_id needs to consume. This is for data dependancy.
{
"name":<string>
"dag":[
{
"node_id": "<string>",
"properties":
{
"node_id_label": "<string>"
"primitive":"<condition | parallel | serial>",
"condition":
{
"source":"<key obtained from node)id result json>",
"operator":"<equals || greater_than || less_than || ..>",
"target":"<string|integer>"
},
"next": "<next node_id to be executed : if primitive=parallel, "next" will take list of node_ids, if primitive: serial then specify a single node_id >",
"branch_1": "<node_id if type==condition else keep "">",
"branch_2": "<node_id if type==condition else keep "">",
"arguments": {} ---> Keep it blank for all action. It will get updated when the DAG is run
"outputs_from": "<list>"
}
},
{
},
.
.
.
{
}
]
}
Sample Example Usage
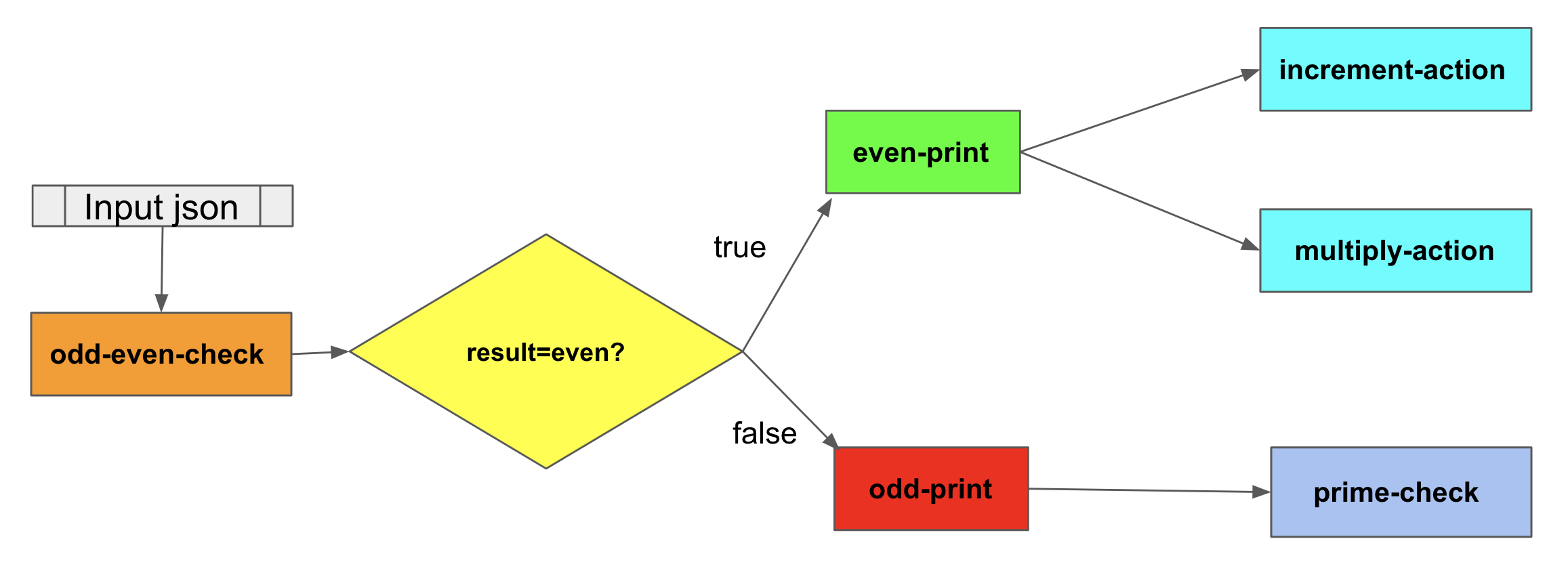
{
"name": "odd-even-test",
"dag": [
{
"node_id": "odd-even-action",
"properties":
{
"label": "Odd Even Action",
"primitive": "condition",
"condition":
{
"source":"result",
"operator":"equals",
"target":"even"
},
"next": "",
"branch_1": "even-print-action",
"branch_2": "odd-print-action",
"arguments": {},
"outputs_from":[]
}
},
{
"node_id": "even-print-action",
"properties":
{
"label": "Even Print Action",
"primitive": "parallel",
"condition": {},
"next": ["increment-action","multiply-action"],
"branch_1": "",
"branch_2": "",
"arguments":{},
"outputs_from":["odd-even-action"]
}
},
{
"node_id": "increment-action",
"properties":
{
"label": "INCREMENT ACTION",
"primitive": "serial",
"condition": {},
"next": "",
"branch_1": "",
"branch_2": "",
"arguments":{},
"outputs_from":["even-print-action"]
}
},
{
"node_id": "multiply-action",
"properties":
{
"label": "MULTIPLY ACTION",
"primitive": "serial",
"condition": {},
"next": "",
"branch_1": "",
"branch_2": "",
"arguments":{},
"outputs_from":["even-print-action"]
}
},
{
"node_id": "odd-print-action",
"properties":
{
"label": "Odd Print Action",
"primitive": "serial",
"condition":{},
"next": "prime-check-action",
"branch_1": "",
"branch_2": "",
"arguments":{},
"outputs_from":["odd-even-action"]
}
},
{
"node_id": "prime-check-action",
"properties":
{
"label": "Prime Check Action",
"primitive": "serial",
"condition":{},
"next": "",
"branch_1": "",
"branch_2": "",
"arguments":{},
"outputs_from":["odd-print-action"]
}
}
]
}
Handle output from multiple actions
Suppose you want to merge outputs from two actions action_1 and action_2 in your action_3, then you must include the following lines in your action_3 to process incoming inputs from action_1 and action_2
. This is applicable for merging primitive as well as handling output from multiple actions.- "key_action_1" refers to a key from action_1 response which you want to use in action_3
- "key_action_2" refers to a key from action_2 response which you want to use in action_3
params = json.loads(sys.argv[1])
op_1 = params["__ow_body"][0]["key_action_1"]
op_2 = params["__ow_body"][1]["key_action_2"]
Use these op_1 and op_2 to process